Infographic Transcript
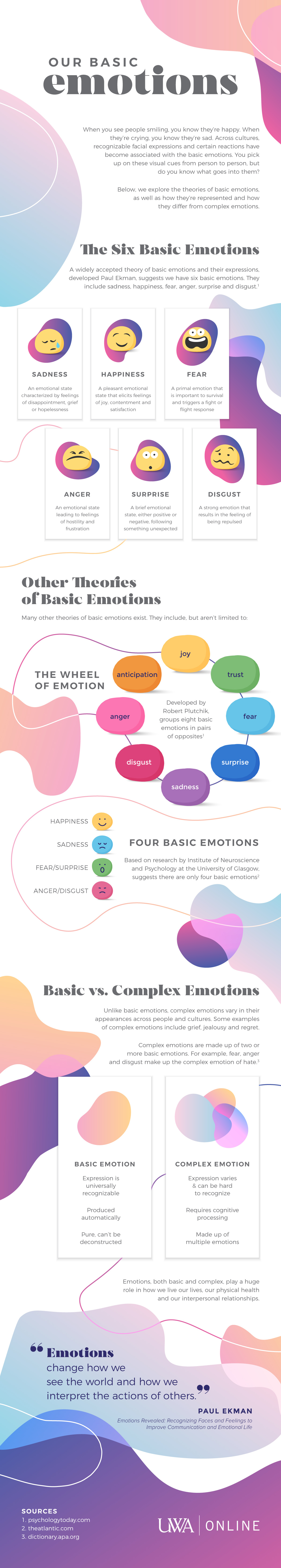
When you see people smiling, you know they’re happy. When they’re crying, you know they’re sad. Across cultures, recognizable facial expressions and certain reactions have become associated with the basic emotions. You pick up on these visual cues from person to person, but do you know what goes into them?
Below, we explore the theories of basic emotions, as well as how they’re represented and how they differ from complex emotions.
Begin or Advance Your Psychology Career
Explore DegreesThe Six Basic Emotions
A widely accepted theory of basic emotions and their expressions, developed Paul Ekman, suggests we have six basic emotions. They include sadness, happiness, fear, anger, surprise and disgust. [1]
Sadness
An emotional state characterized by feelings of disappointment, grief or hopelessness
Expression: Frown, loss of focus in eyes, tears
Happiness
A pleasant emotional state that elicits feelings of joy, contentment and satisfaction
Expression: Smile, laughter
Fear
A primal emotion that is important to survival and triggers a fight or flight response
Expression: Wide eyes, tense stretched lips
Anger
An emotional state leading to feelings of hostility and frustration
Expression: Glare, eyebrows drawn together, tight lips
Surprise
A brief emotional state, either positive or negative, following something unexpected
Expression: Raised brows, open mouth, gasp
Disgust
A strong emotion that results in feeling repulsed
Expression: Wrinkled nose, gagging, no eye contact
Other Theories of Basic Emotions
Many other theories of basic emotions exist. They include, but aren’t limited to:
- The Wheel of Emotion: Developed by Robert Plutchik, groups eight basic emotions in pairs of opposites [1]
Joy-Sadness
Anger-Fear
Trust-Distrust
Surprise-Anticipation
- Four Basic Emotions: Based on research by Institute of Neuroscience and Psychology at the University of Glasgow, suggests there are only four basic emotions [2]
Happiness
Sadness
Fear/Surprise
Anger/Disgust
Basic vs. Complex Emotions
Unlike basic emotions, complex emotions vary in their appearances across people and cultures. Some examples of complex emotions include grief, jealousy and regret.
Complex emotions are made up of two or more basic emotions. For example, fear, anger and disgust make up the complex emotion of hate. [3]
| Basic Emotion | Complex Emotion |
| Expression is universally recognizable | Expression varies & can be hard to recognize |
| Produced automatically | Requires cognitive processing |
| Pure, can’t be deconstructed | Made up of multiple emotions |
Emotions, both basic and complex, play a huge role in how we live our lives, our physical health and our interpersonal relationships.
“Emotions change how we see the world and how we interpret the actions of others.” – Paul Ekman, “Emotions Revealed: Recognizing Faces and Feelings to Improve Communication and Emotional Life”
The study of basic emotions is far from complete. Interested in learning more about theories of emotion and emotions’ effect on humans psychologically and physically? Consider an online psychology degree from the University of West Alabama. If you already hold a bachelor’s in psychology, consider our online master’s in experimental psychology. At UWA, you’ll earn your degree entirely online at one of the state’s most affordable institutions. Our culturally and intellectually diverse institution and flexible structure allow you to challenge yourself while still fitting education into your busy lifestyle.
Sources
- psychologytoday.com
- theatlantic.com
- dictionary.apa.org